As a general rule, here and there, we have all heard good things about the sweet potato. Or because it was recommended to us by a friend or even our personal trainer. But why are sweet potatoes so beneficial?
Let’s go in parts:
Nutritional Composition
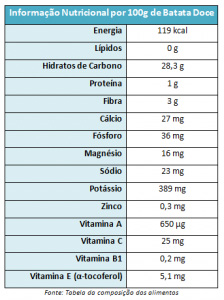
On consulting the list of PGI (Protected Geographical Indication) products provided by the European Union, we can read that “an average-sized sweet potato provides twice the amount of vitamin A and a third of the vitamin C we need daily”. And indeed, the vitamin and mineral concentration it presents is immense. In fact, when compared to the other potato, the sweet potato has twice as much vitamin C, five times as much vitamin E, far more vitamin A (those beta-carotenes that give sweet potatoes their orange colour), twice as much calcium and twenty-three times less sodium . (See table).
Its antioxidant richness strengthens our immune system and prevents the development of certain pathological conditions such as cholesterol or cancer. In addition, sweet potatoes are known to prevent dietary deficiencies all over the world.
Sweet potatoes are also a source of complex carbohydrates with a low glycaemic index, which means that the absorption of this nutrient in the body is slow, allowing glucose to enter the bloodstream slowly without increasing insulin levels. This is one of the reasons why sweet potatoes are one of the favourite foods of bodybuilders. In addition, several studies have shown that low glycaemic index foods are more effective in weight loss and in the control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, by reducing insulin resistance. Another of sweet potato’s advantages is its fibre content which promotes satiety and therefore decreases appetite.
Culinary versatility
Traditionally, in Portugal, sweet potatoes are eaten baked or boiled. However, there are other ways of consuming them, such as in mashed potatoes, soup, tortillas, etc. We can also make appetizers from the peel and include its leaves in our meals, as in a sauté, for example.
Summarizing
The sweet potato:
– It is a good source of energy for training;
– Prevents dietary deficiencies due to its vitamin and mineral concentration;
– It has an antioxidant action on the organism;
– It is a satiating food;
– It decreases insulin resistance due to its low glycaemic index.

References:
1. Tabela da composição dos alimentos. Instituto Nacional Ricardo Jorge.
2. Dias, C.; Silveira, M. Actividade antioxidante de diferentes hortofrutícolas da Ilha Terceira. 2010.
3. Ludvik B, et al. Mode of action of ipomoea batatas (Caiapo) in type 2 diabetic patients. Metabolism. Julho de 2003;52(7):875-80.
4. Thomas DE, Elliott EJ, Baur L. Low glycaemic index or low glycaemic load diets for overweight and obesity. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3).
5. Imagem 1: Natalie Maynor
6. Imagem 2: A Repository




